Maternal Dietary Omega 3 Fatty Acids And Placental Function
Request pdf maternal dietary omega 3 fatty acids and placental function the developing fetus requires substantial amounts of fatty acids to support rapid cellular growth and activity.
Maternal dietary omega 3 fatty acids and placental function. 1 school of anatomy physiology human biology the university of western australia perth western australia australia. Maternal dietary omega 3 fatty acids and placental growth and function i preface the experimental work presented in this thesis was undertaken in the school of anatomy physiology and human biology the university of western australia under the supervision of prof. Maternal dietary omega 3 fatty acid supplementation reduces placental oxidative stress and increases fetal and placental growth in the rat. Our objective was to determine the effects of supplementation of these two nutrients during late gestation on fetal growth dna methylation and mrna expression of genes associated with the inflammatory response and dna.
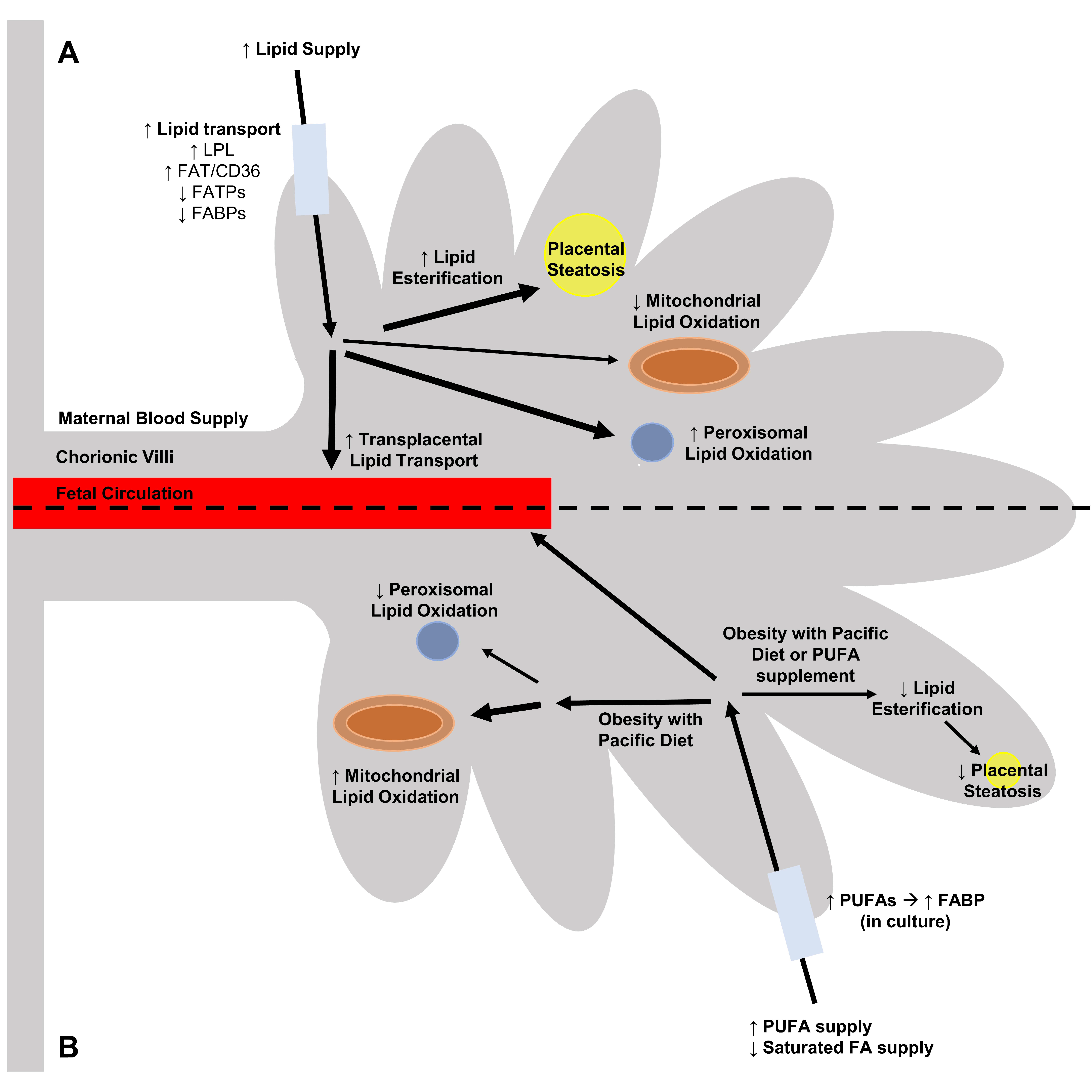
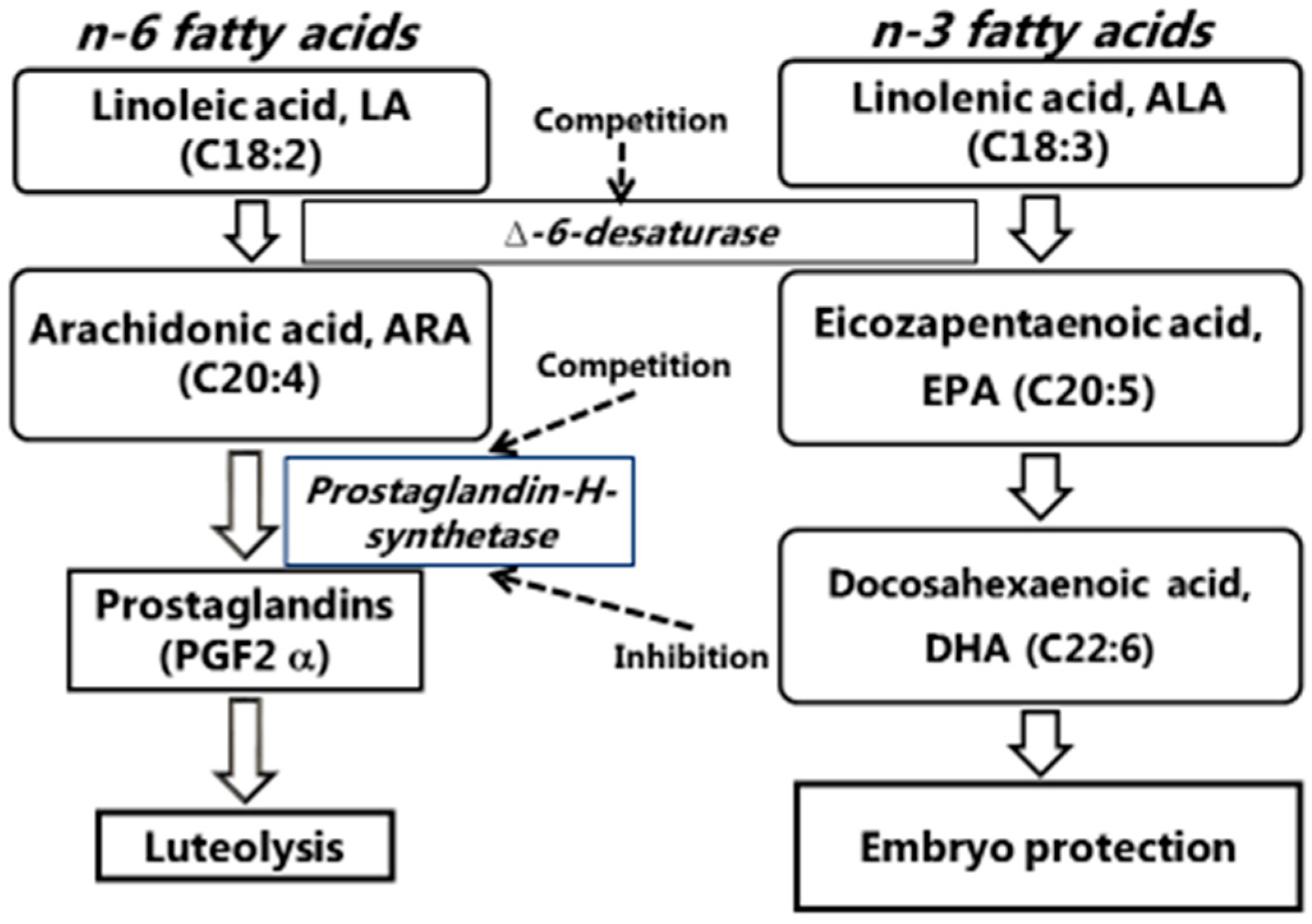
The maternal fetal and neonatal efa lcpufas status is an important determinant of feto placental growth and development 30 32 the critical requirement of these fatty acids in feto placental unit demands an efficient transport of these lcpufas to the fetus by the placenta. Although the fatty acid composition delivered to the fetus is largely determined by maternal circulating levels the placenta preferentially transfers physiologically important long chain polyunsaturated fatty acids lc pufas particularly omega 3 n 3 pufas. Jones ml 1 mark pj mori ta keelan ja waddell bj. However the effect of both nutrients on fetal development has not been explored.
Omega 3 pufa or methionine met supply during gestation alters offspring physiology. The developing fetus requires substantial amounts of fatty acids to support rapid cellular growth and activity. Fatty acids are important biological constituents that serve a range of structural energetic and signaling roles the developing fetus requires substantial amounts of fatty acids to support rapid cellular growth and activity and among these the omega 3 n 3 polyunsaturated fatty acids pufas are particularly important although subject to some controversy maternal dietary.