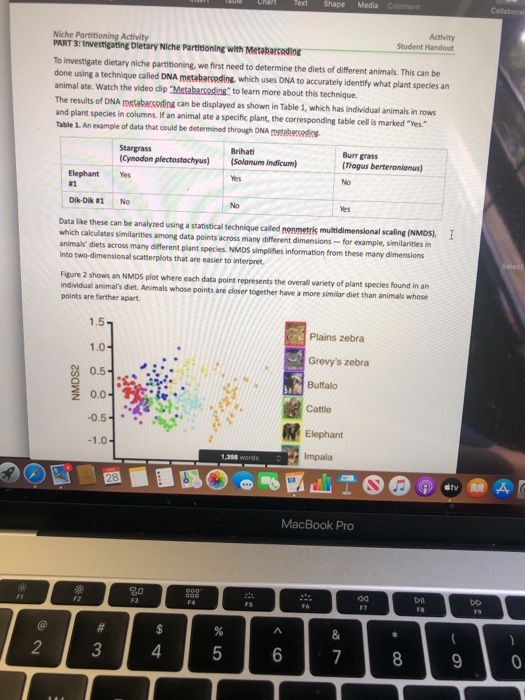
Dietary Niche Partitioning Example

Type spatial niche partitioning description species occupy different spaces dietary niche partitioning niche partitioning by resource height species eat different things species access different resources at different example antelope species live in different places herbivores such as zebras eat mostly grass giraffes usually eat from the.
Dietary niche partitioning example. Organisms feed on the same resource but at different times. These dietary differences in conjunction with spatial associations observed by shakeri 2010 suggest that during the winter spring and summer p. Niche partitioning by plant height. Evidence on niche partitioning dietary seasonality and potentially even fallback food consumption.
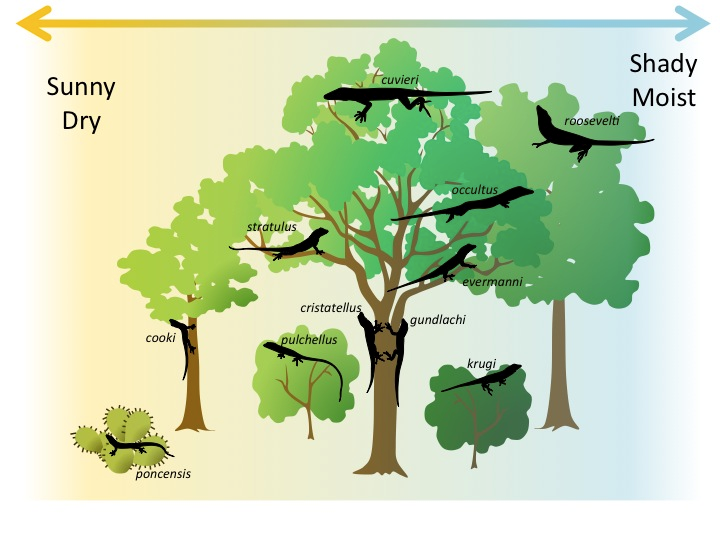
For example taller animals eat from the higher parts of the tree. 2017 showed that the acorn production in the previous year had a positive effect on the population abundance of a. Boylii are able to coexist on the ferp through a combination of dietary niche partitioning and spatial partitioning. This clip is from a 2015 holiday lecture series patterns and processes in ecology.
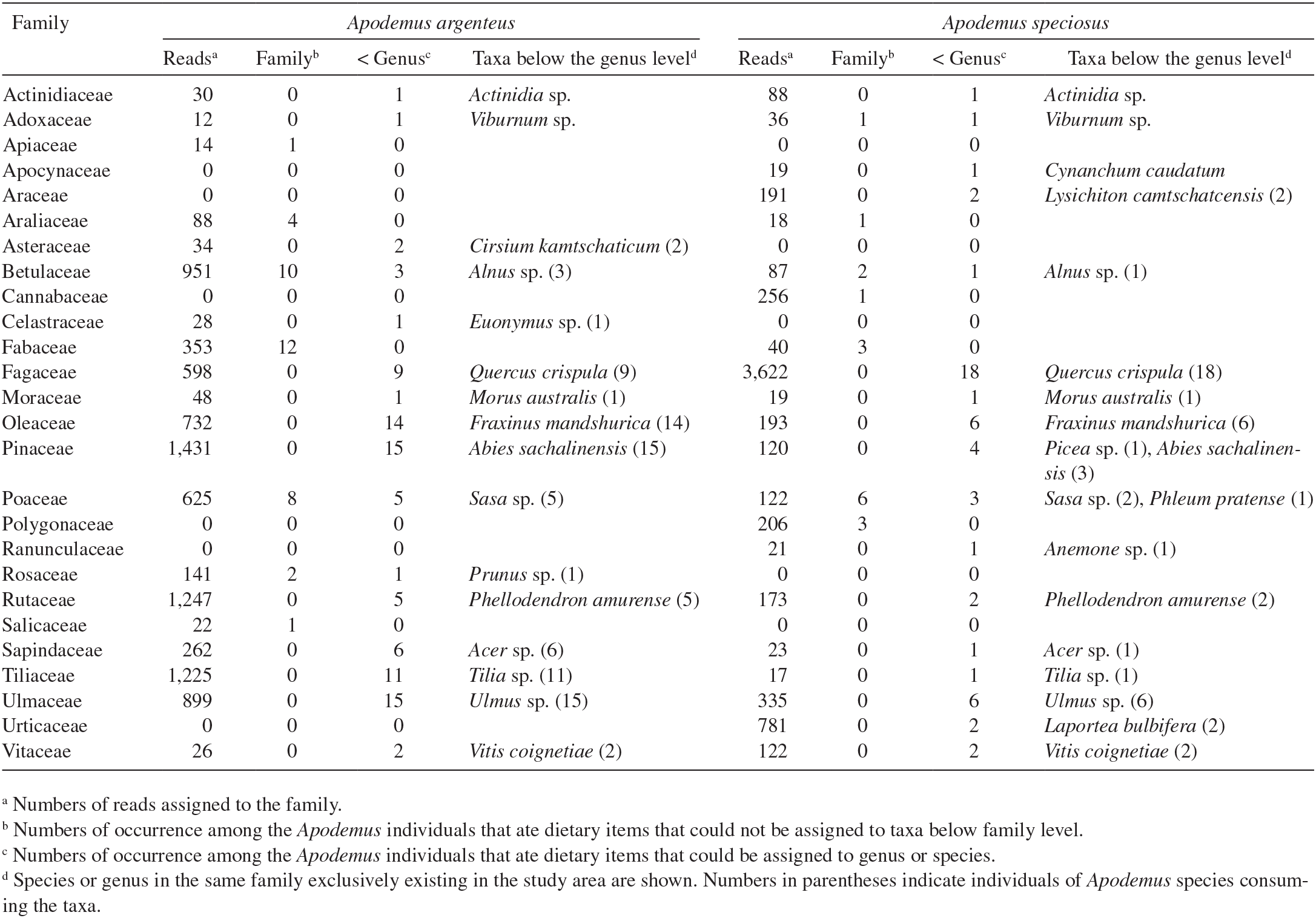
Therefore dietary profiles for these species remain to be fully determined and consequently niche partitioning according to a fine scale resolution of diet has not been demonstrated. Niche partitioning subsequently reduces both the dietary niche breadth of the population. Speciosus while that. Niche partitioning is predicted to be greatest under low resource availability when spe cies focus on the resource they can best extract which decreasesthe diversity of food items in their diets.
Niche partitioning by time and grass height. The roles of morphological traits resource variation and resource partitioning associated with the dietary niche expansion in the fish eating bat myotis pilosus yang chang jilin provincial key laboratory of animal resource conservation and utilization northeast normal university changchun china. To date d13c values have been analyzed in fossil tooth enamel of many african hominin taxa revealing high levels of inter specific dietary diversity in the reli ance on c4 and c3 plants van der merwe et al 2008. Niche partitioning abrams 1983.
Spatial partitioning dietary partitioning plant height partitioning list three common. Grazer browser spectrum animals are eating different things. He provides examples of herbivores partitioning their habitat by space spatial niche partitioning and diet dietary niche partitioning the latter of which may involve dividing food resources based on time or height. Coexistence of ecologically similar species is sustained by niche partitioning a fundamental element of which is diet.
Its diet where it lives when it migrates when it sleeps which of the following is the competitive exclusion principle. Overlapping of resource requirements between sympatric species can create interspecific competitive or facilitative effects on the foraging behaviour of herbivores.