Dietary Functions Of Lipids

As discussed in the carbohydrates chapter glucose is stored in the body as glycogen.
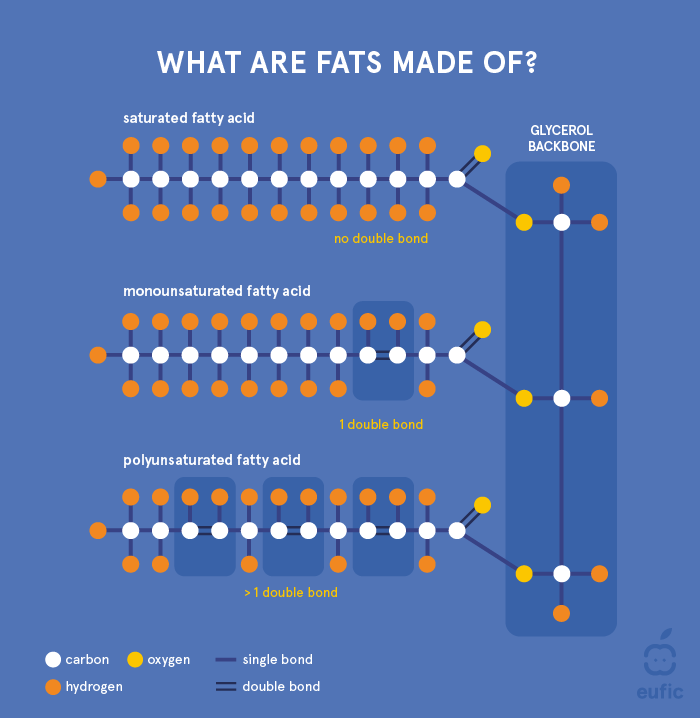
Dietary functions of lipids. At 9 calories per gram compared to 4 calories per gram of carbohydrates and proteins fats serve as concentrated sources of energy to fuel your active lifestyle. Most of the energy required by the human body is provided by carbohydrates and lipids as discussed in the carbohydrates chapter glucose is stored in the body as glycogen while glycogen provides a ready source of energy lipids primarily. Most of the energy required by the human body is provided by carbohydrates and lipids. They encompass fatty acids saturated monounsaturated and polyunsaturated the latter further categorised as omega 3 or omega 6 fatty acids their derivatives including mono di and triglycerides and phospholipids as well as sterols such as cholesterol.
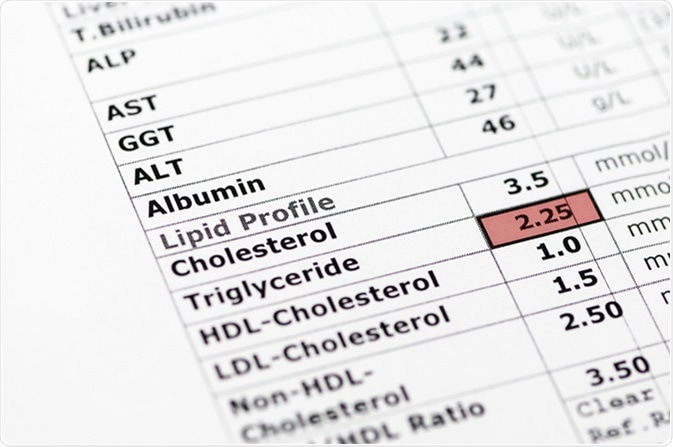
This chapter first summarizes the relation between these lipid sensitive markers and cardiovascular risk. Lipid any of a diverse group of organic compounds including fats oils hormones and certain components of membranes that are grouped together because they do not interact appreciably with water. The excess energy from the food we eat is digested and incorporated into adipose tissue or fatty tissue. The five functions of lipids include.
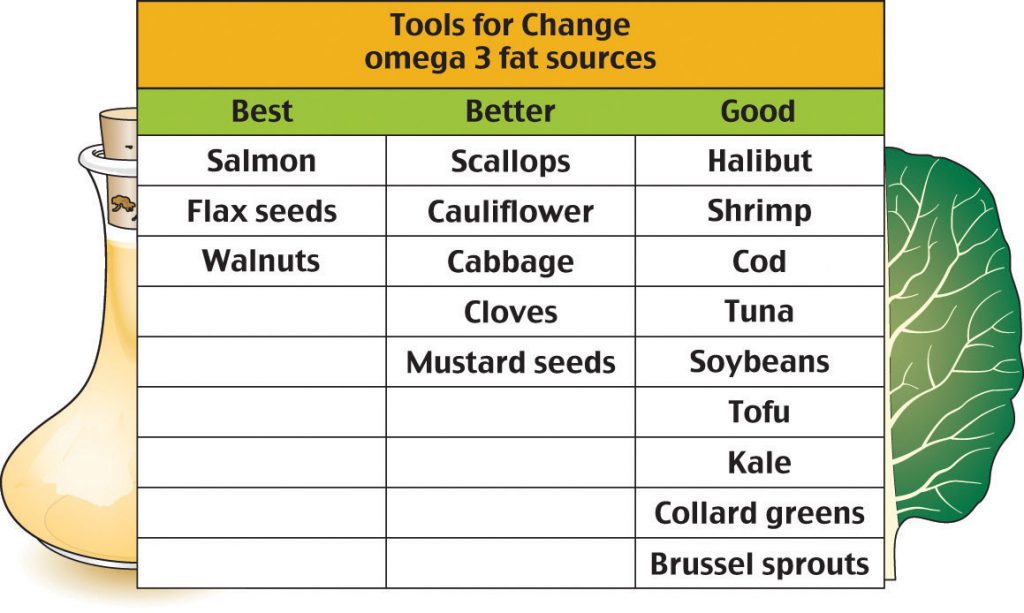
Discuss the functions of essential fatty acids such as omega 3 and where to find them in foods. Dear colleagues dietary lipids derived from plants and animals are essential for growth and development and serve as an energy reserve. Explain the relationship of dietary lipids to chronic disease. Acting as an energy source although the body uses carbohydrates as its primary form of energy it can turn to lipids when it needs a reserve.
Digestion and absorption of lipids lipids are large molecules and generally are not water soluble like carbohydrates and protein lipids are broken into small components for absorption since most of our digestive enzymes are water based how does the body break down fat and make it available for the various functions it must perform in the human body. Most people weighing 154 pounds have enough lipids to carry them through 24 to 30 days without food. Lipids are utilized by the living organism. The functions of lipids in the body storing energy.
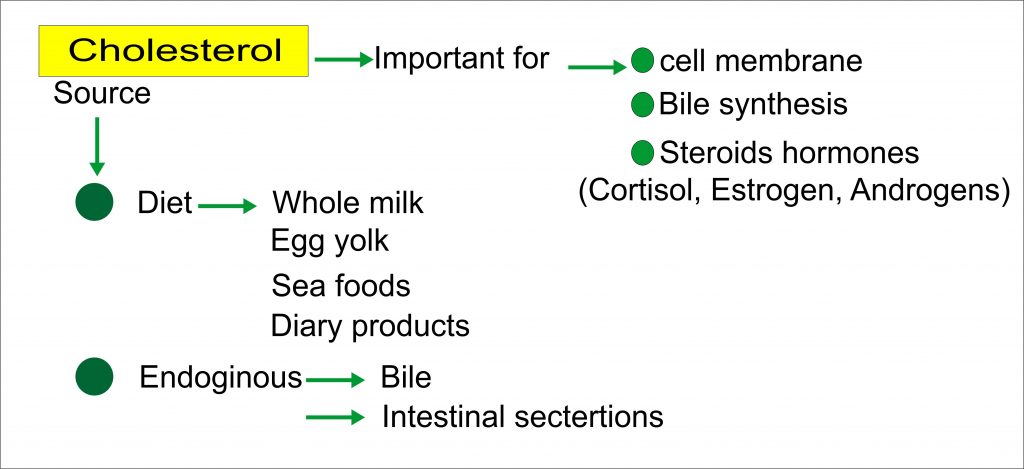
The functions of lipids in the body storing energy. Lipids a chemical family that includes cholesterol and fat make up a major part of the average human diet. Lipids have some relations to fatty acids e g. Identify foods high in monounsaturated polyunsaturated saturated fatty acids trans fatty acids and cholesterol.
Lipid is soluble in the solvent like ether chloroform benzene etc. Lipids can be defined as insolubility in water but soluble in nonpolar solvents commonly termed as fats. Learn more about the structure types and functions of lipids in this article. The excess energy from the food we eat is digested and incorporated into adipose tissue or fatty tissue.