Dietary Lipids Gut Microbiota And Lipid Metabolism

Here we investigated how interaction between gut microbiota and dietary lipids regulates lipid composition in the liver and plasma and gene expression in the liver.
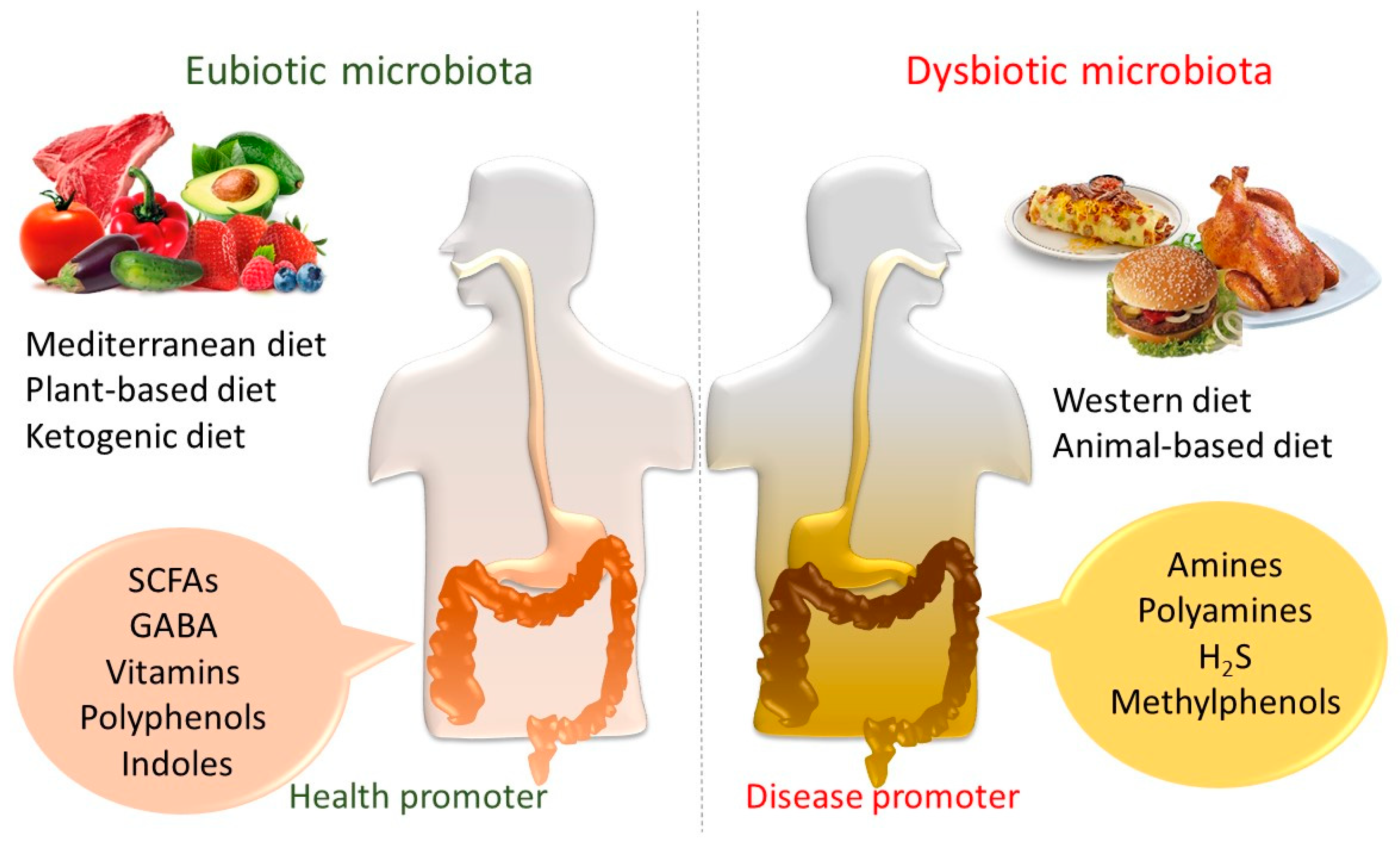
Dietary lipids gut microbiota and lipid metabolism. The composition and function of the gut microbiota is dynamic and affected by diet properties such as the amount and composition of lipids. To further investigate how dietary lipids and gut microbiota affect wat inflammation metabolism we performed a microarray analysis of wat from conv r and gf mice fed a lard or fish oil diet. Risk factors of coronary heart disease include levels of. We have previously shown that the presence of a gut microbiota remodels lipid composition.
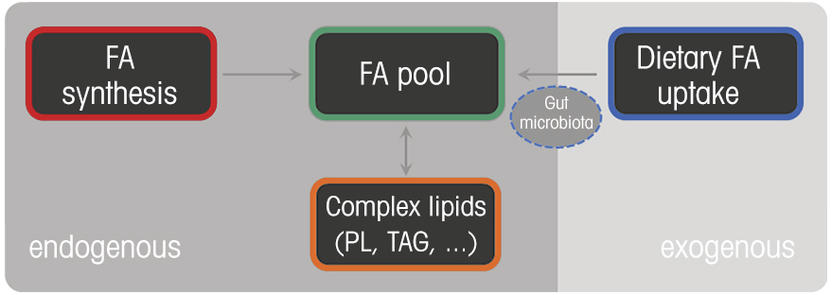
The gut microbiota is a central regulator of host metabolism. The gut microbiota is a central regulator of host metabolism. Lipids affect the gut microbiota both as. Lipids affect the gut microbiota both as substrates for bacterial metabolic processes and by inhibiting bacterial growth by toxic influence.
The gut microbiota modulates host lipid metabolism velagapudi et al 2010. The gut microbiota is a central regulator of host metabolism. The gut microbiota host lipid metabolism and cardiovascular disease coronary heart disease is a major cause of death in western society. 1 the gut microbiota processes dietary nutrients into metabolites and 2 the diet affects the gut microbiota composition and thereby its meta bolic potential and impact on the host.
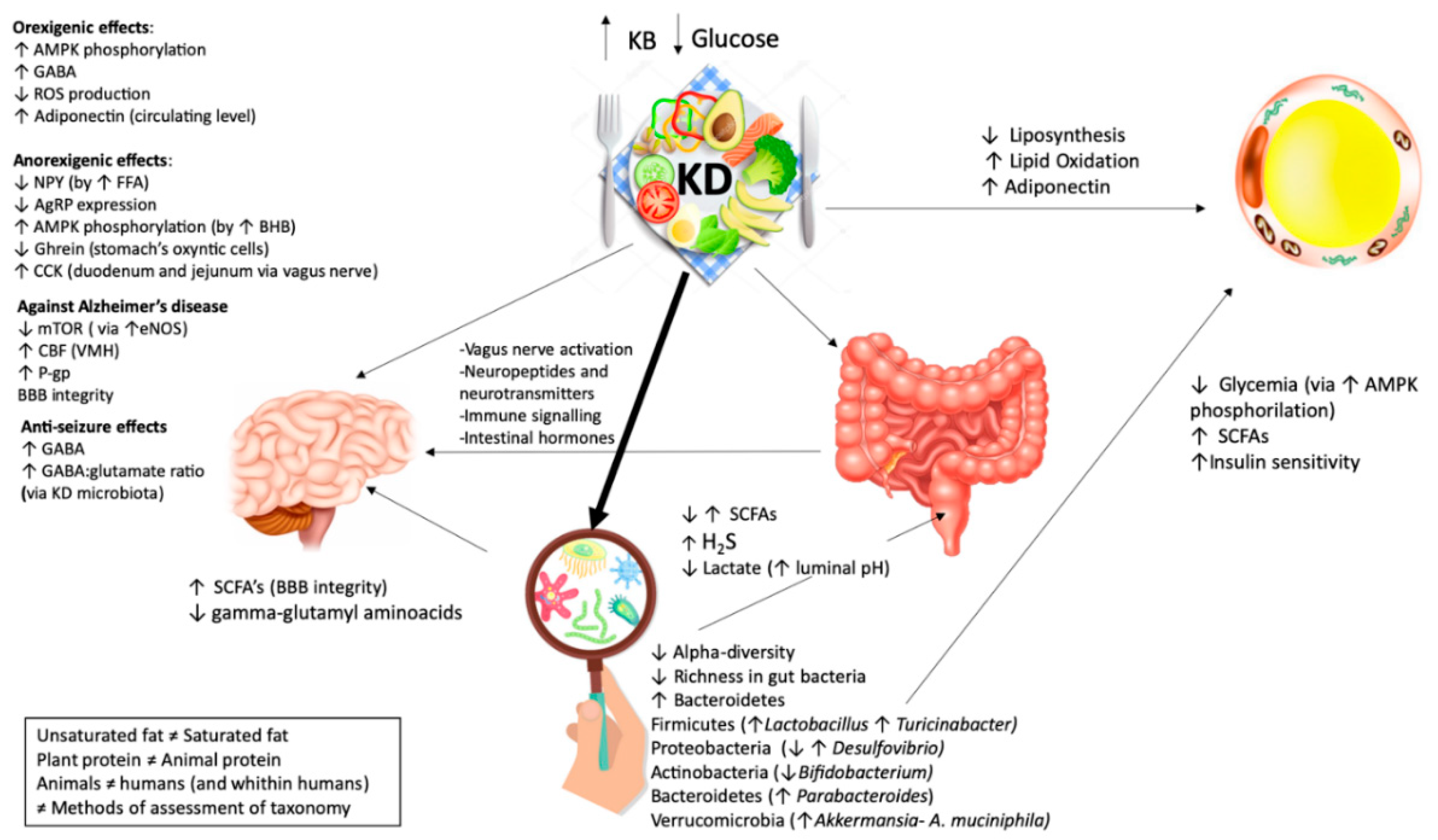
Hence dietary lipids may influence host physiology through interaction with the gut microbiota. Therefore protection against wat inflammation in myd88 and trif mice fed lard might be due to decreased tlr signaling induced by ligands originating from the host or from the diet. Hence dietary lipids may influence host physiology through interaction with the gut microbiota. The gut microbiota has been shown to affect lipid metabolism and lipid levels in blood and tissues both in.
Hence dietary lipids may influence host physiology through interaction with the gut microbiota. The composition and function of the gut microbiota is dynamic and affected by diet properties such as the amount and composition of lipids. Lipids affect the gut microbiota both as substrates for bacterial metabolic processes and by. Hence dietary lipids may influence host physiology through interaction with the gut microbiota.
Principal component analysis of gene expression data revealed that mice separated on diet in the first dimension and on microbial status in the second. Output of the gut microbiota because. The composition and function of the gut microbiota is dynamic and affected by diet properties such as the amount and composition of lipids. Lipids affect the gut microbiota both as substrates for bacterial metabolic processes and by.
In particular the im portance of dietary fibers for gut microbiota composition and function has been extensively studied.