Dietary Energy Source Dairy Cows

In a lactating cow the rumen microbes will typically supply some metabolizable protein if there are adequate fermentable carbohydrates and nitrogen supplied in the diet.
Dietary energy source dairy cows. 1 adaptation physiology group wageningen institute of animal sciences wageningen university po box 338 6700 ah wageningen the. Effect of dietary energy source on energy balance production metabolic disorders and reproduction in lactating dairy cattle. Energy cannot be measured with chemicals in a laboratory. The values in these and other published tables are estimates of the energy delivered to lactating cows consuming.
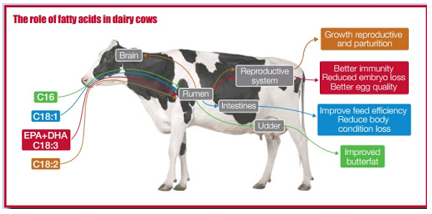
Consequently many dairy nutritionists are searching for alternative energy sources not only due to the current price. After water energy is the largest nutrient requirement of the dairy cow. However in recent months these er energy sources that can be used in the lactating cow diet. To test the effect of lipogenic and glucogenic nutrients on energy partitioning energy balance and nitrogen balance of 16 lactating dairy cows were determined by indirect calorimetry in climate respiration chambers from wk 2 to 9 postpartum.
Offered a good economical source of fat to meet the energy needs of lactating cows. Dry matter energy crude protein fiber and non fiber carbohydrate concentrations of some feedstuffs commonly fed to dairy cattle a has typical values for me ne l ne m and ne g for some feedstuffs commonly fed to dairy cows. Since energy comes from the digestion of carbohydrates protein and fat researchers attempt to predict the energy value of feeds based on the amount of each and their assumed or measured digestibility and availability to the cow. Since dry cow diets are low in energy and fermentable carbohydrates especially starch rumen undegradable protein rup product typically needs to be included in the diet in.
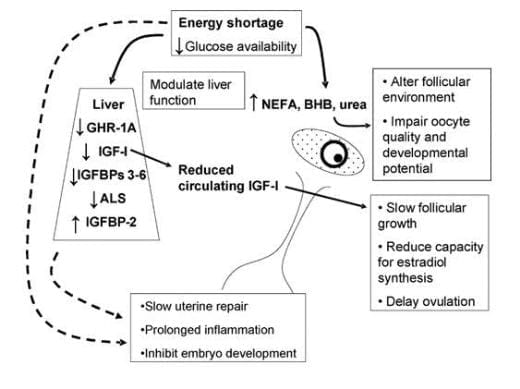
Van knegsel at 1 van den brand h dijkstra j tamminga s kemp b. Metabolic problems related to negative energy balance suggest a role for the balance in supply of lipogenic and glucogenic nutrients. Several reports indicated that energy sources could be manipulated via ingredients in the diet to prevent or treat peripartum neb and improve the fertility of dairy cows staples et al 1998 gong. Enhancing the fat content of lactation diets is a convenient means to raise dietary energy density and intake which in turn helps support the heightened energy demands of modern high producing dairy cows.