Excess Dietary Protein Fate

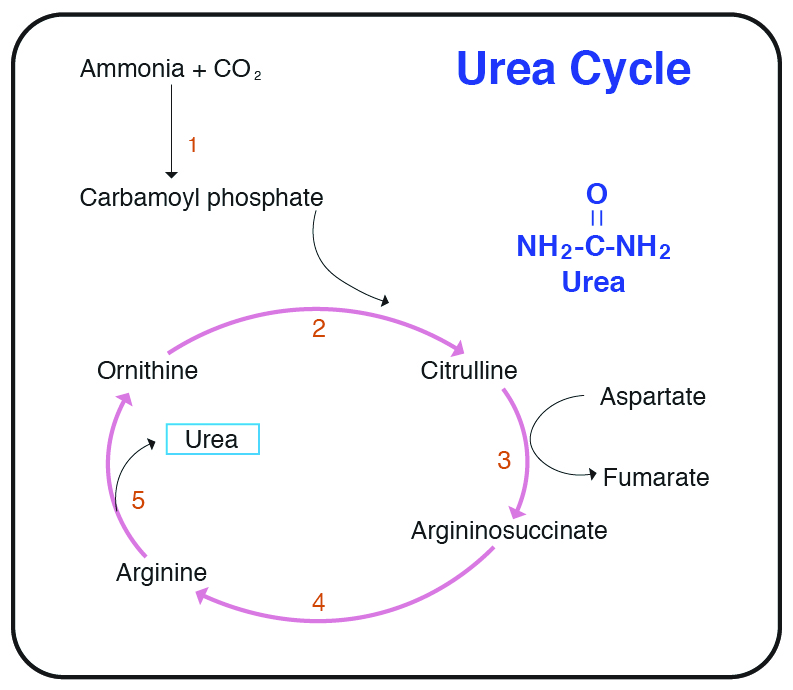
Which of the following leads to the production of urea.
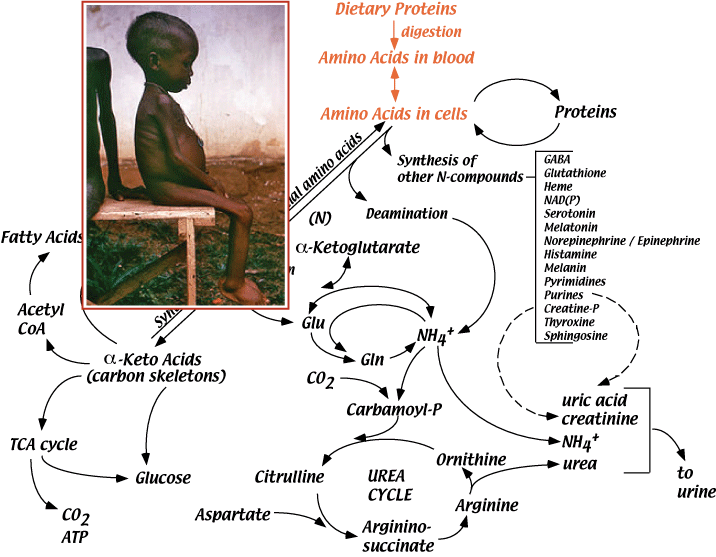
Excess dietary protein fate. This fat is stored in the adipose tissues and can be used by the body during lean times. What is the fate of excess intake of dietary protein. A the liver will store the extra amino acids. Oxidation of amino acids c.
A high protein low carb diet may help your extra pounds weight fly off initially but it can actually cause weight gain in the long term according to a spanish study to come to this finding. This fat is stored in the adipose tissues and can be used by the body during lean times. It helps to build and repair muscle organs and bones. We conclude that excessive dietary protein from.
What is the fate of excess dietary protein after absorption. D extra proteins will be synthesized and stored in skeletal muscle. What is the immediate fate of excess dietary protein in the body. Protein is an essential part of a healthy diet.
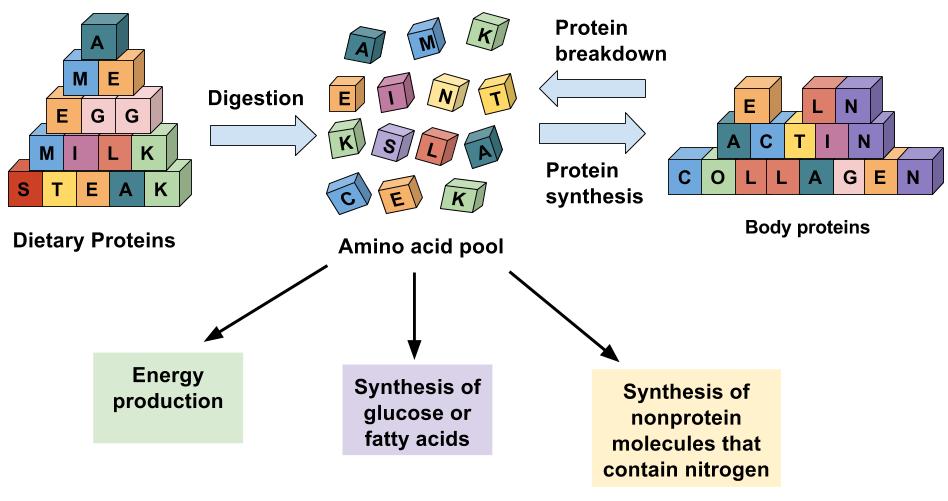
Essential amino acid balance. What is the fate of excess dietary protein. Dietary protein has many important bodily functions including repairing and building bones muscles and organs. The most common outcome is for the building and maintenance of lean tissues such as muscle and bone as well as the skin and hair.
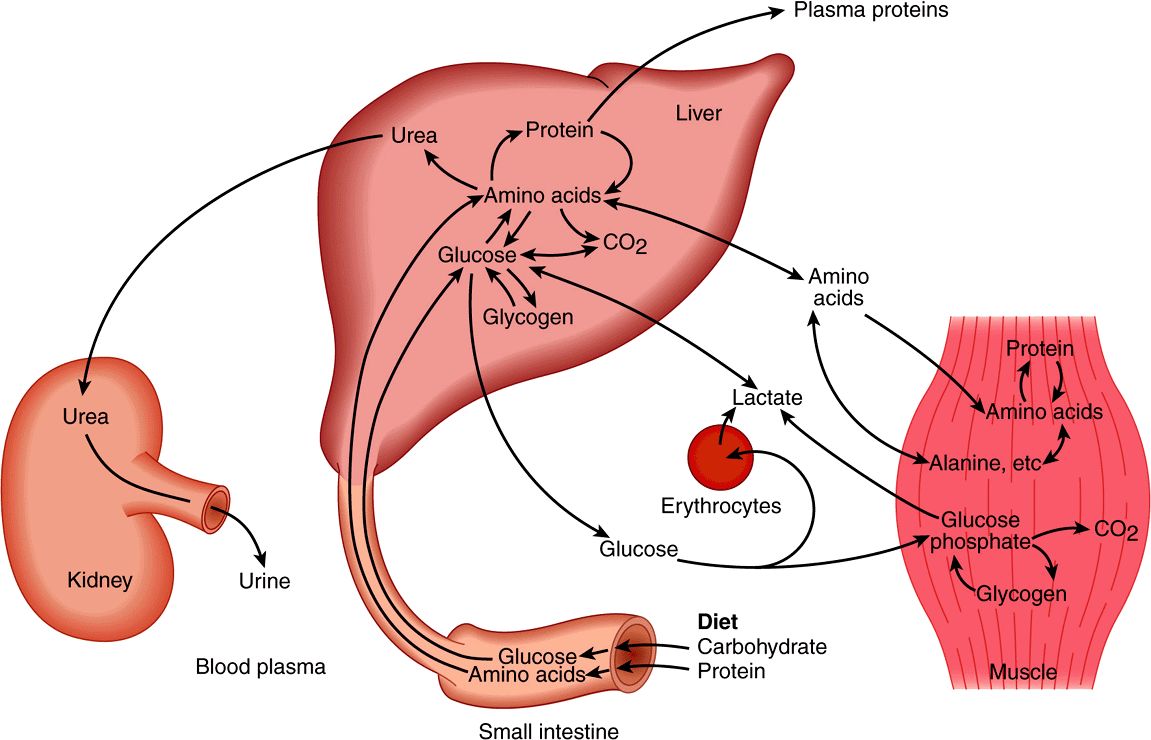
Excess protein is converted to fat. Excess protein is converted to fat. Synthesis of protein from amino acids 9. B the liver will rapidly degrade the extra amino acids.
Foods with high potential renal acid load adversely affects bone unless buffered by the consumption of alkali rich foods or supplements. After absorption the extra amino acids will be rapidly degraded. Proteins when broken down to their component peptides or amino acids have a number of different fates. C it will be excreted as urinary amino acids.
With all the latest diet crazes you may be wondering what happens if you eat too much protein. What is the fate of excess intake of dietary protein. Which of the following is the most likely side effect of a high protein low. What is the fate of excess dietary protein.
Effects of excess protein. Oxidation of glucose b.