Dietary Magnesium And C Reactive Protein Levels

Meta analysis and systematic review.
Dietary magnesium and c reactive protein levels. Dietary magnesium and c reactive protein levels. Current dietary guidelines recommend adequate intake of magnesium 310 420 mg daily in order to maintain health and lower the risk of cardiovascular disease. Magnesium is an essential mineral with several dietary sources including whole grains green leafy vegetables legumes and nuts as a critical cofactor for hundreds of enzymes and a direct antagonist of intracellular calcium intracellular magnesium. The objective of this study was to determine whether dietary magnesium consumption is associated with c.
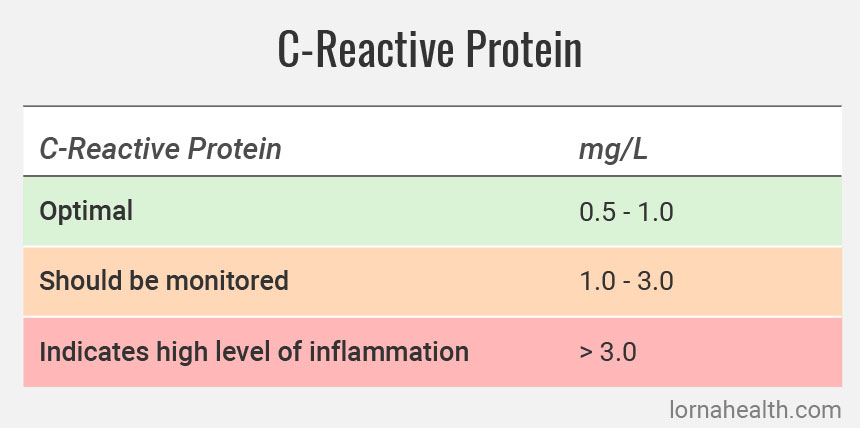
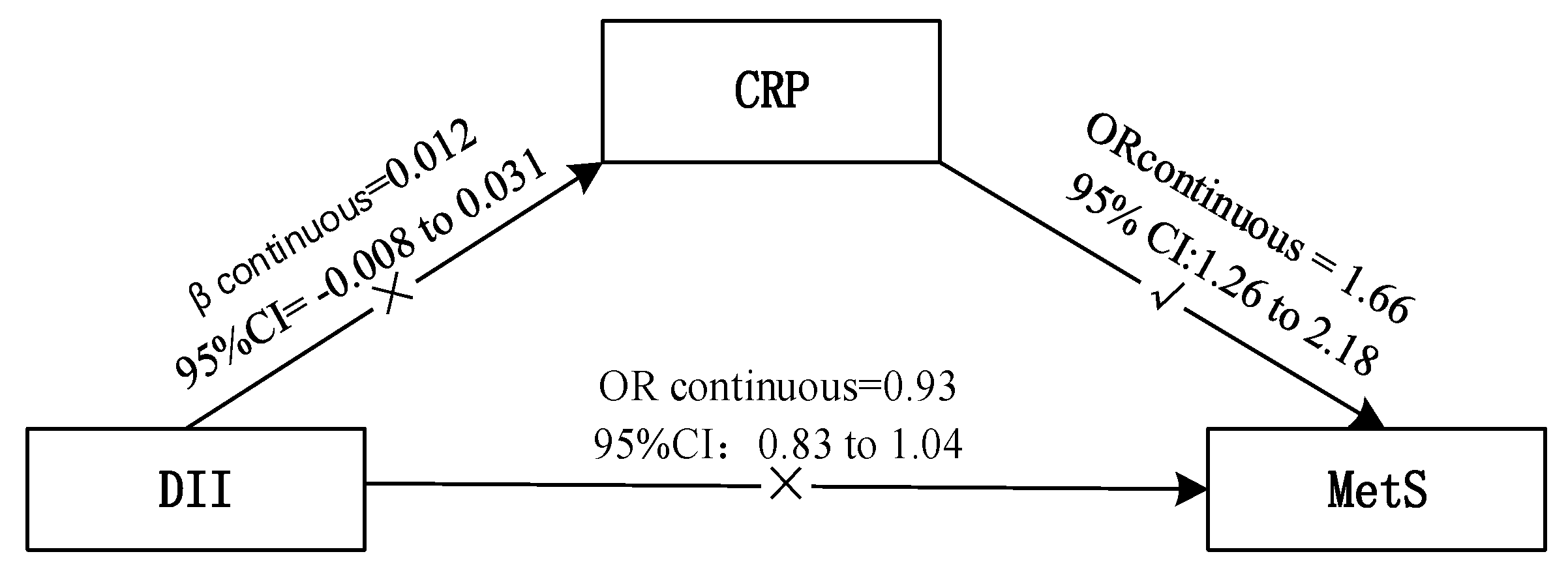
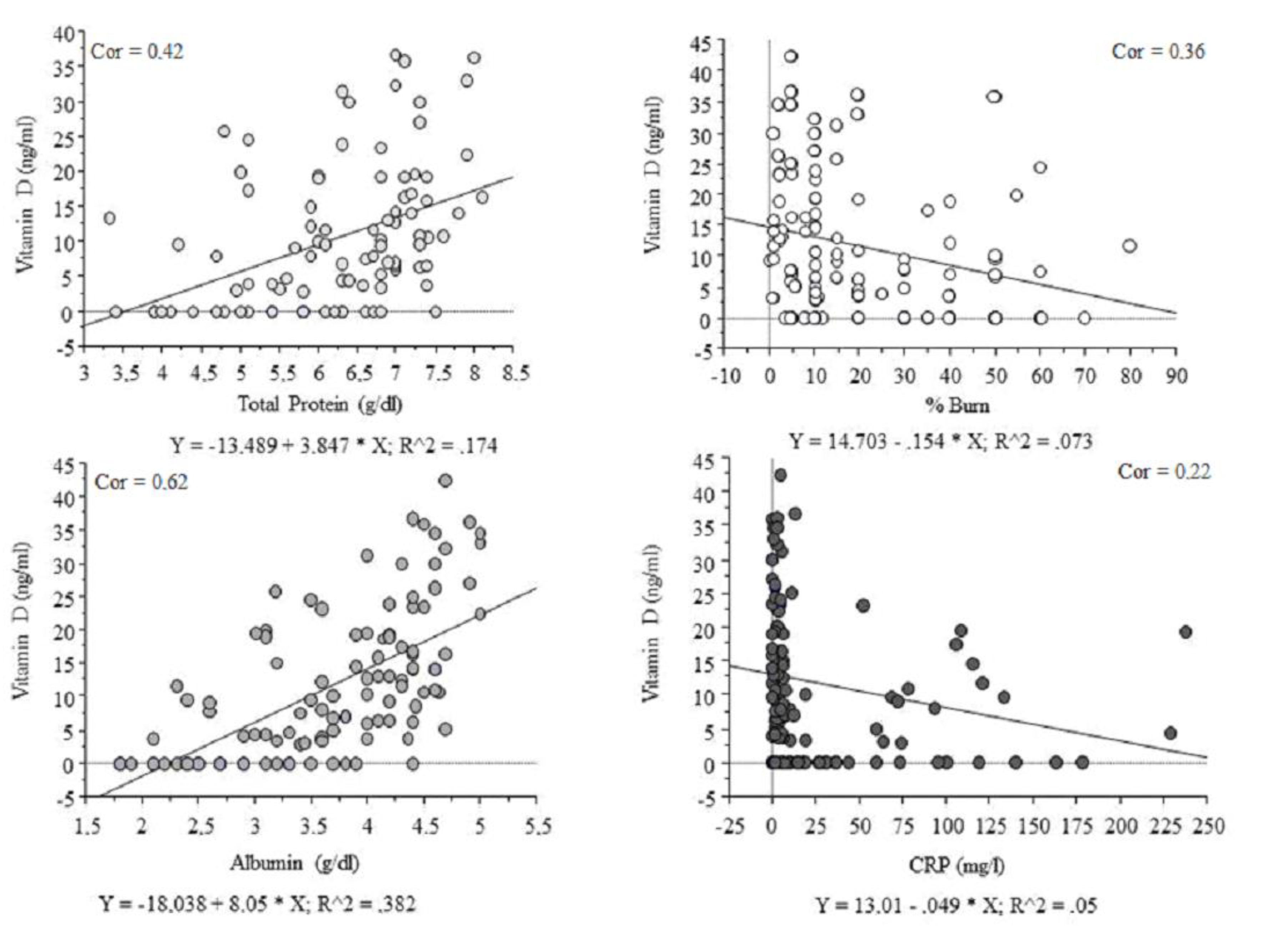
18 june 2014 dietary magnesium intake is inversely associated with serum c reactive protein levels. Whs women s health study. Eur j clin nutr. Many earlier studies proved that dietary magnesium intake is inversely correlated with serum c reactive protein crp which is an established biomarker of inflammation 14 15 16 17 18.
D t dibaba 1. 510 516 view in article. Recent evidence from animal and clinical studies suggests that magnesium may be associated with inflammatory processes. Eur j clin nutr 2014.
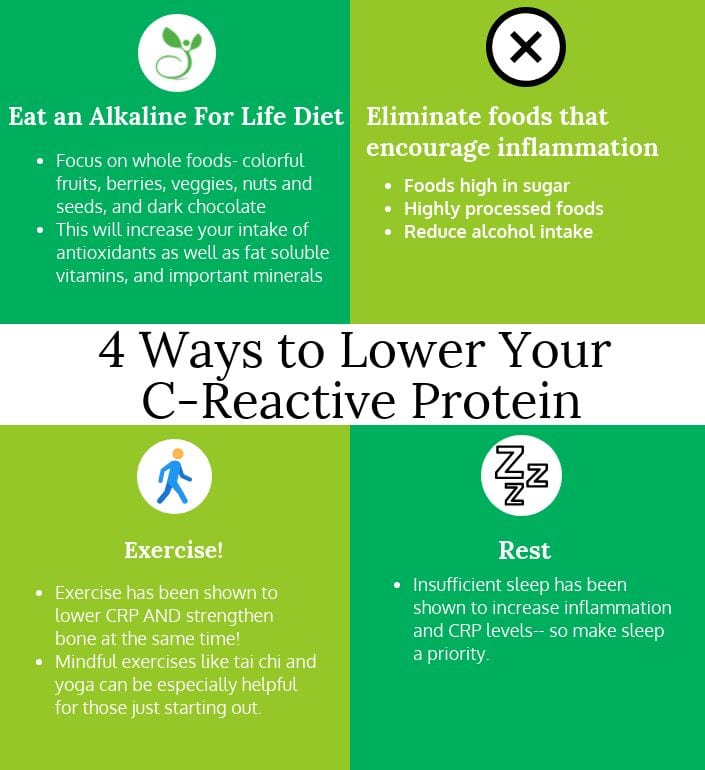
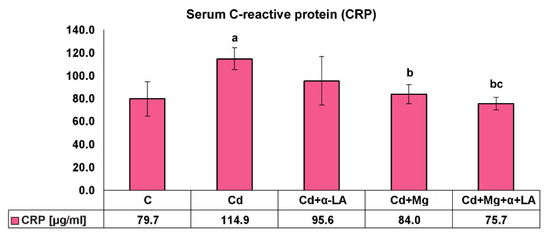
To study whether low dietary magnesium mg intake and serum high sensitivity c reactive protein hs crp predict the development of clinical knee osteoarthritis oa. The objective of this study was to determine the likelihood of elevated c reactive protein crp in people taking magnesium containing supplements of 50 mg d or more. The mediterranean diet includes foods that are beneficial for lowering inflammation and thus c reactive protein levels in the body. This diet contains fresh whole foods including fruits and vegetables whole grains and fish which supply anti inflammatory omega 3 fatty acids.
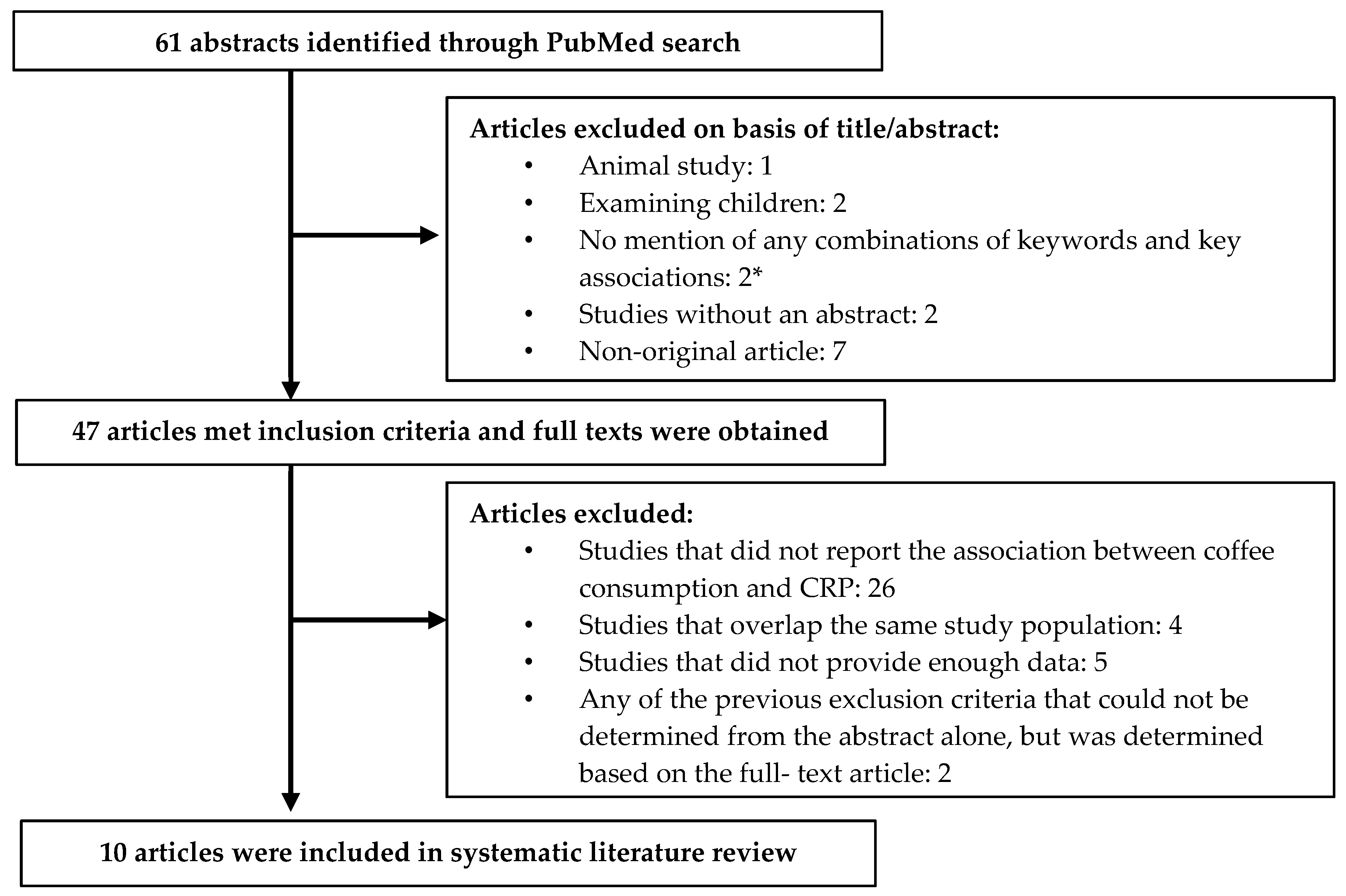
We examined this issue in a study sample derived from the national health and nutrition examination survey 1999 2002 a nationally representative survey of the civilian. Dietary magnesium intake is inversely associated with serum c reactive protein levels. Methods the cohort consisted of 4 953 participants of a national health examination survey who were free of knee and hip oa at baseline. Meta analysis and systematic review.
Meta analysis and systematic review.