Dietary Boron Intake And Prostate Cancer Risk

Scientists from the university of california los angeles school of public health compared the diets of 76 men diagnosed with prostate cancer to the diets of 7 751 healthy males.
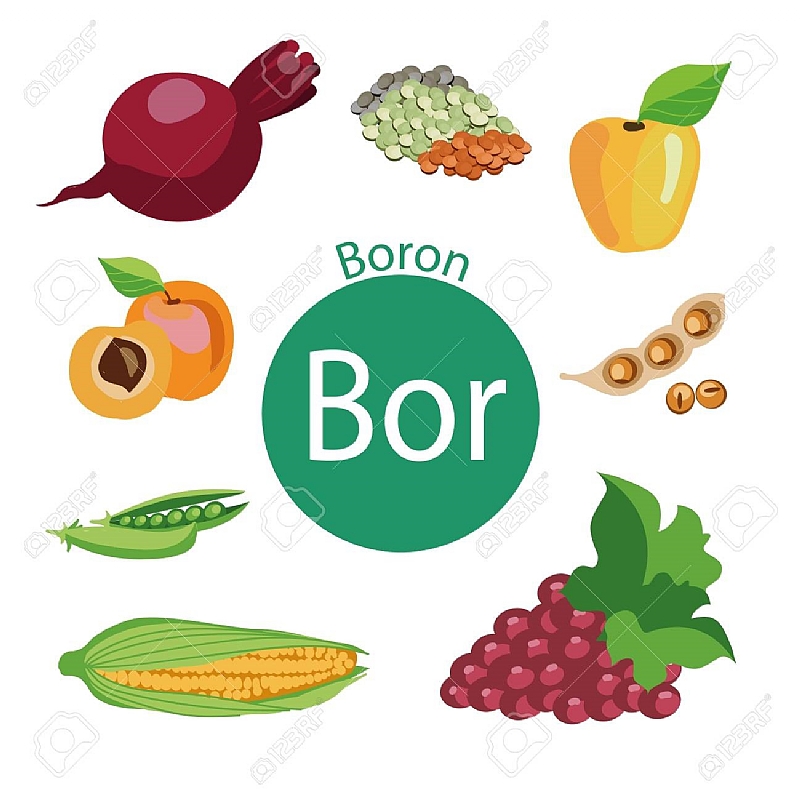
Dietary boron intake and prostate cancer risk. Boron affects human steroid hormone levels. However the association between dietary boron intake and the risk of prostate cancer has not been evaluated by any epidemiological study. The idea that supplemental use of boron might reduce the risk of prostate cancer was first brought to the attention of scientists following a 2001 study on dietary patterns of prostate cancer patients as reported long ago in life extension magazine. Dietary boron intake and total boron from diet food and water and multivitamin supplements were not associated in this study with strong protective benefits to prostate cancer.
However the association between dietary boron intake and the risk of prostate cancer has not been evaluated by any epidemiological study. That study was controlled for many other factors. In 2001 zhang et al study reported the idea that supplemental use of boron might reduce the risk of prostate cancer. This study compared the diets of 76 prostate cancer patients with those of 7 651 men without cancer.
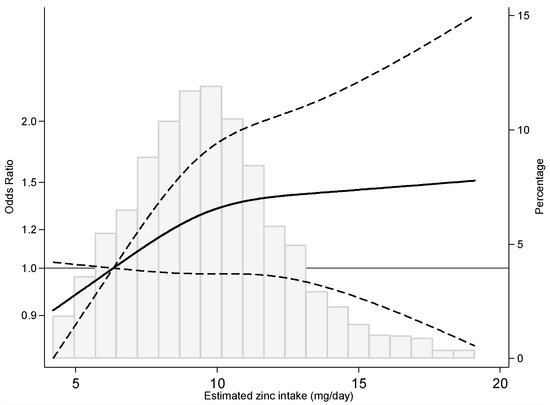
Several observational studies found that boron intakes are inversely associated with prostate cancer risk in men and with lung and cervical cancer risk in women 1 9 41 44. Circulating testosterone and estradiol levels have been proposed to modify prostate cancer risk. Circulating testosterone and estradiol levels have been proposed to modify prostate cancer risk. Our analysis was based on data from the third national health.
Boron neutron capture therapy has been used to treat cancer kankaanranta et al 2007 and an increased intake in dietary boron was linked to a decreased risk of prostate cancer cui et al 2004. The results found that men with the highest boron consumption showed a 54 lower risk of prostate cancer compared to those with the lowest intake 6. The study compared the diets of 76 prostate cancer patients with those of 7 651 men without cancer. When the men were divided into four groups based on their.
Boron affects human steroid hormone levels. This study was brought to the limelight after the researchers followed a dietary patterns of prostate cancer patients. However the association between dietary boron intake and the risk of prostate cancer has not been evaluated by any epidemio logical study. New study findings suggest that men who consume high levels of boron a mineral found in fruits vegetables and nuts reduce their risk of prostate cancer.
One such study compared the dietary intake of boron in ninety five prostate cancer patients with that of 8 720 healthy male controls.