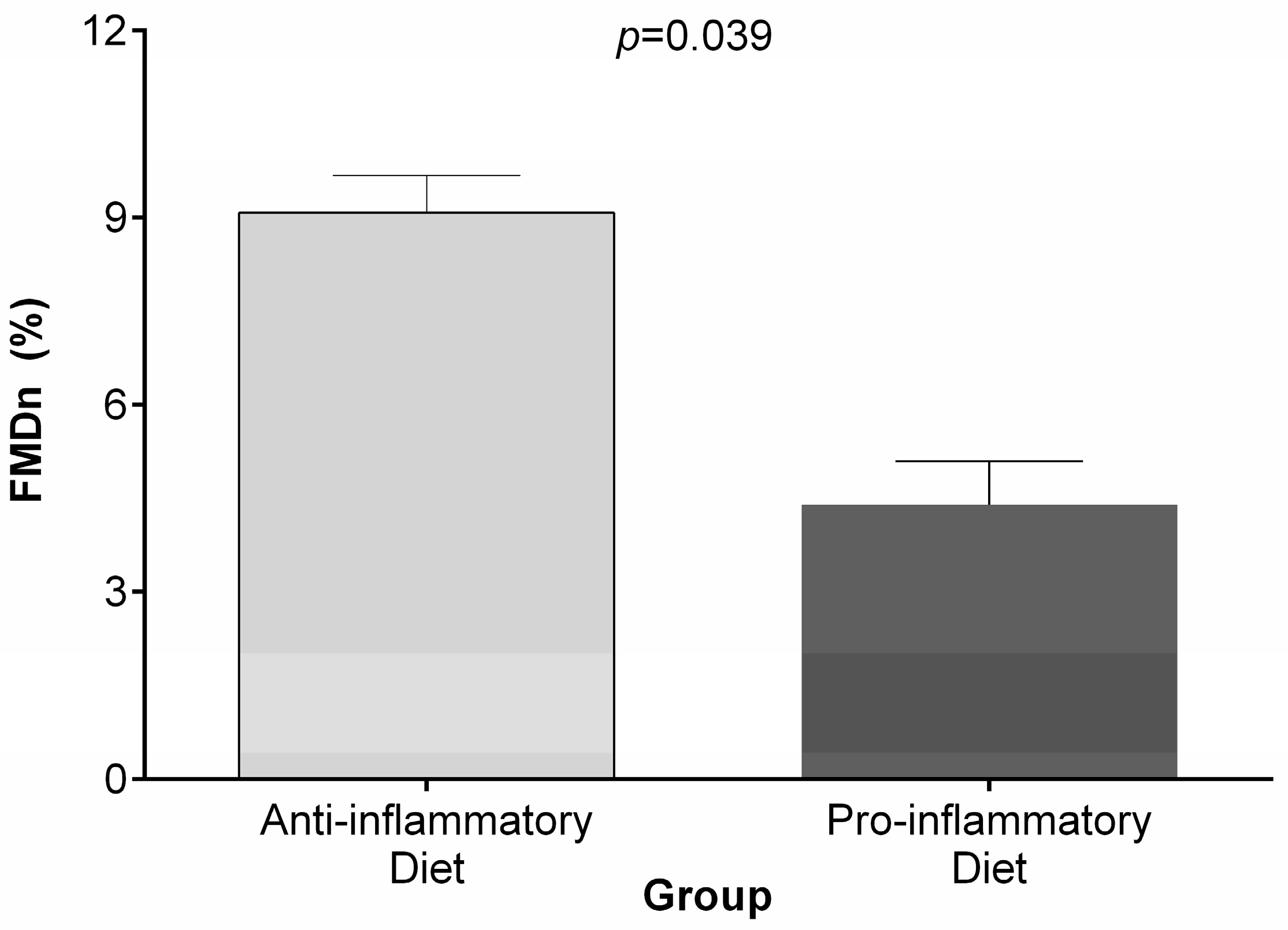
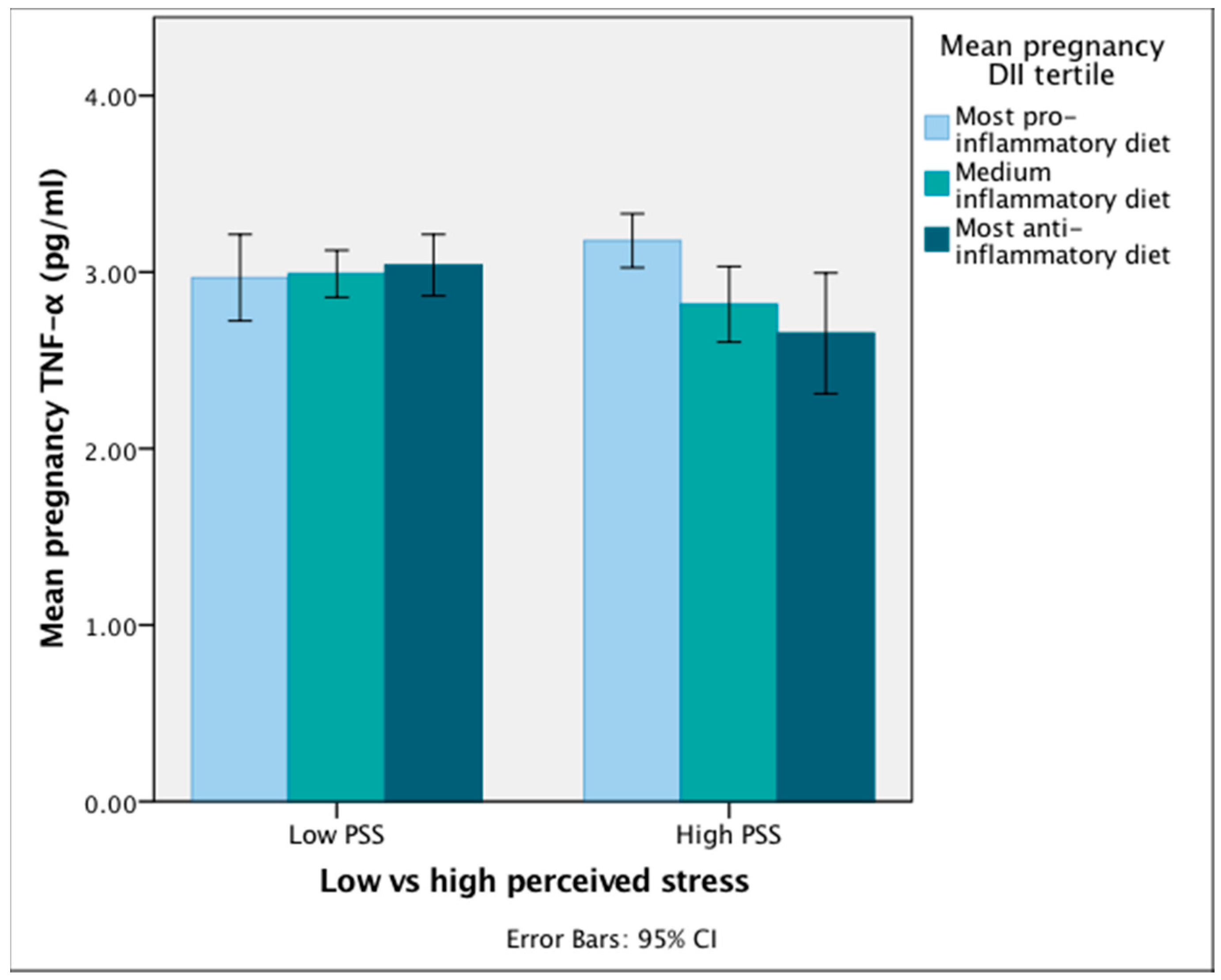
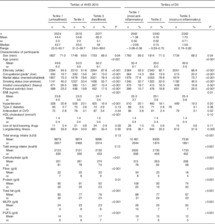
Dietary Inflammatory Index And Depression A Meta Analysis
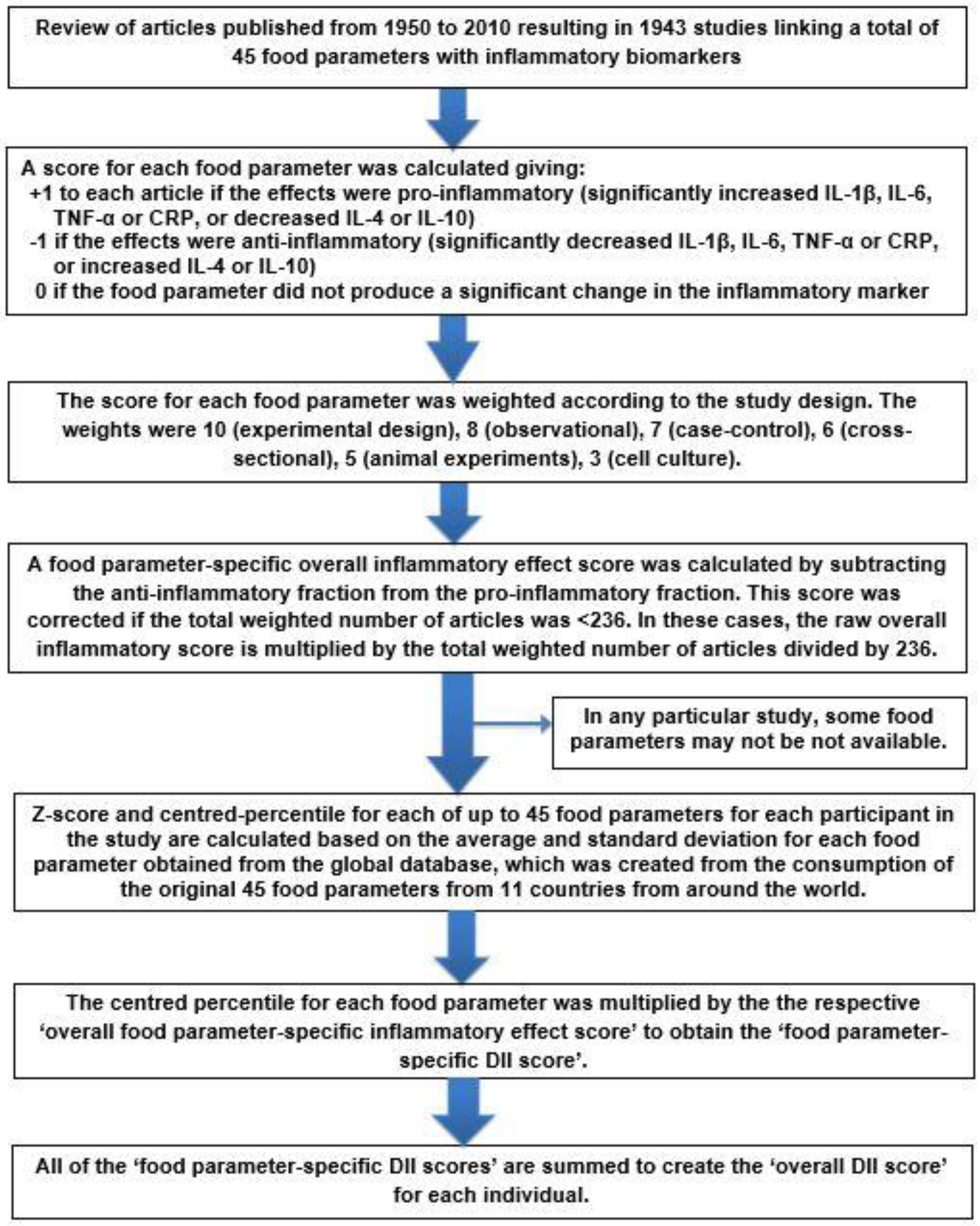
Therefore the inflammatory potential of the diet may also be an etiological factor for these conditions and this may be estimated by calculating the dietary inflammatory index dii score.
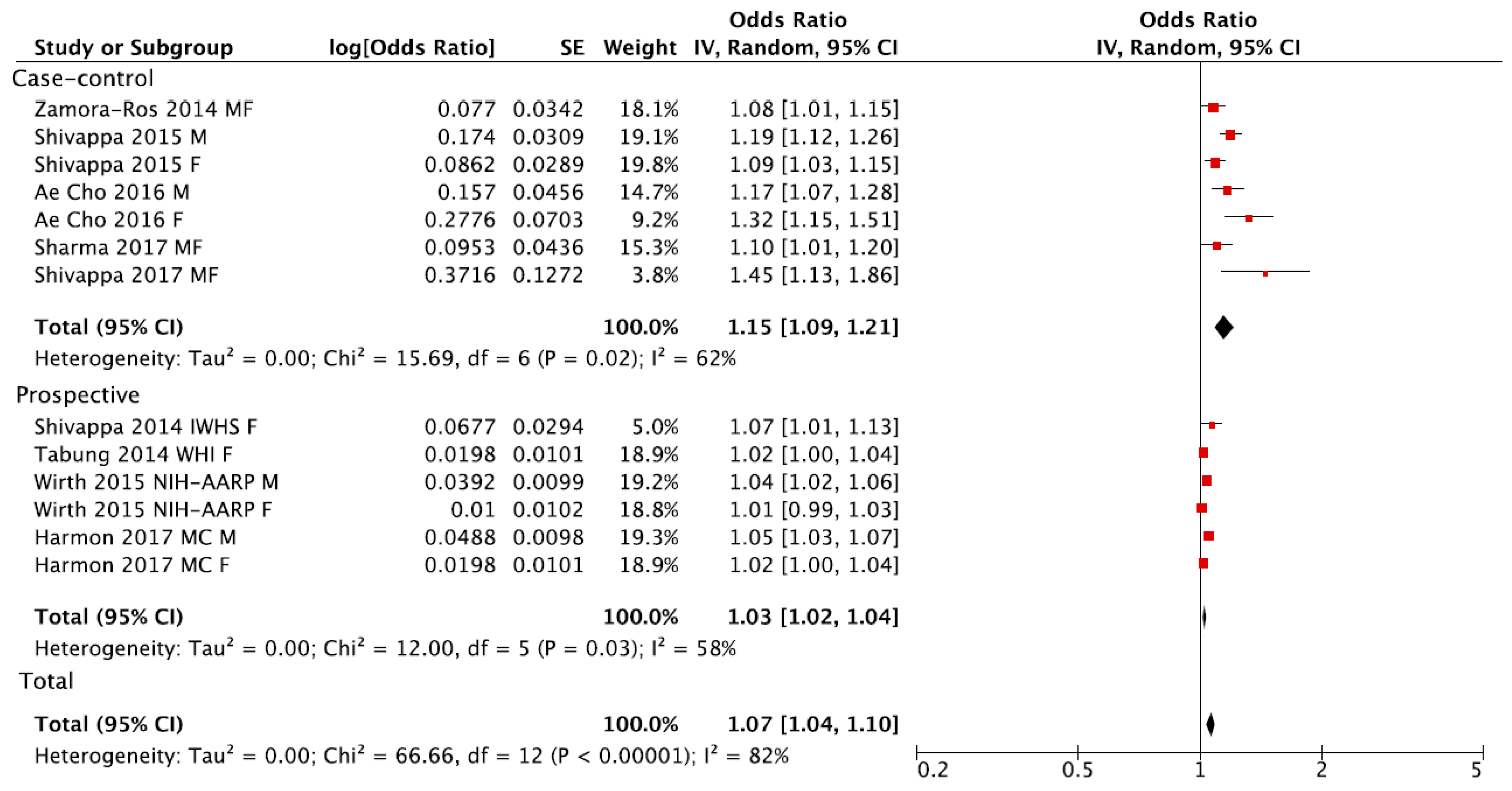
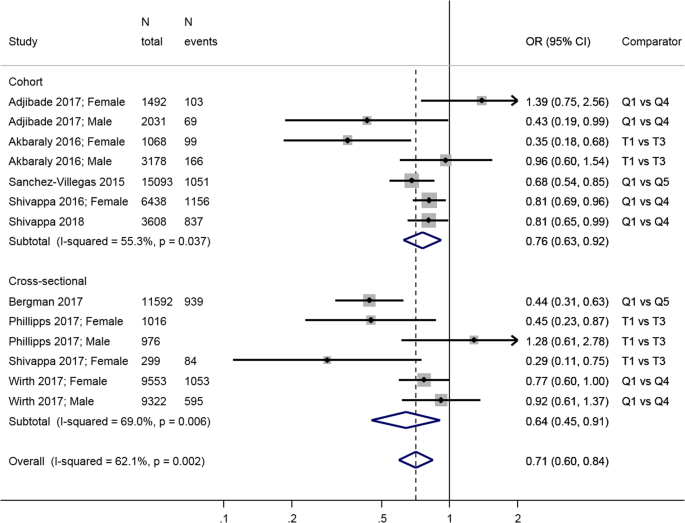
Dietary inflammatory index and depression a meta analysis. A lower dietary inflammatory index was also associated with lower depression incidence in four longitudinal studies relative risk 0 76. A cumulative meta analysis indicated higher levels of. This study aimed to determine the association between dii as a proxy measure of the inflammatory potential of the diet and psychosomatic complaints. Systemic inflammation is emerging as an important factor in the etiology of psychiatric disorders such as depression and anxiety.
There were fewer longitudinal studies using other indices but they and cross sectional evidence also suggest an inverse association between healthy diet and depression e g relative risk. In this meta analysis the authors use a dietary inflammatory index dii to analyze the relation between the inflammatory potential of individual food items and cancer development. A meta analysis showed that a high quality diet regardless of type i e healthy prudent or mediterranean together with a relatively low dietary inflammatory index was associated with a lower risk of depressive symptoms. However more well designed studies are needed to evaluate whether an anti inflammatory diet can reduce the risk of depression.
Although the dietary inflammatory index dii has been evaluated in relation to psychological disorders risk the association between dii and psychosomatic complaints is unclear. We aimed to investigate the association between dii score and incidence. A meta analysis showed that a high quality diet regardless of type i e healthy prudent or mediterranean together with a relatively low dietary inflammatory index was associated with a lower risk of depressive symptoms. The meta analysis suggests that pro inflammatory diet estimated by a higher dii score is independently associated with an increased risk of depression particularly in women.
They find that a higher dii indicative of a more proinflammatory diet was associated with substantial increases in cancer incidence odds of cancer and cancer. In fact a newly conducted meta analysis about dietary inflammatory index dii and depression shed new light on what to eat to fight against depression and why a md is a better choice than wd. This cross sectional study included 2818 people from the general.